Identification of Ions by Chemical and Spectroscopic Means
(chemistry only)
Chemical Analysis
Flame Tests
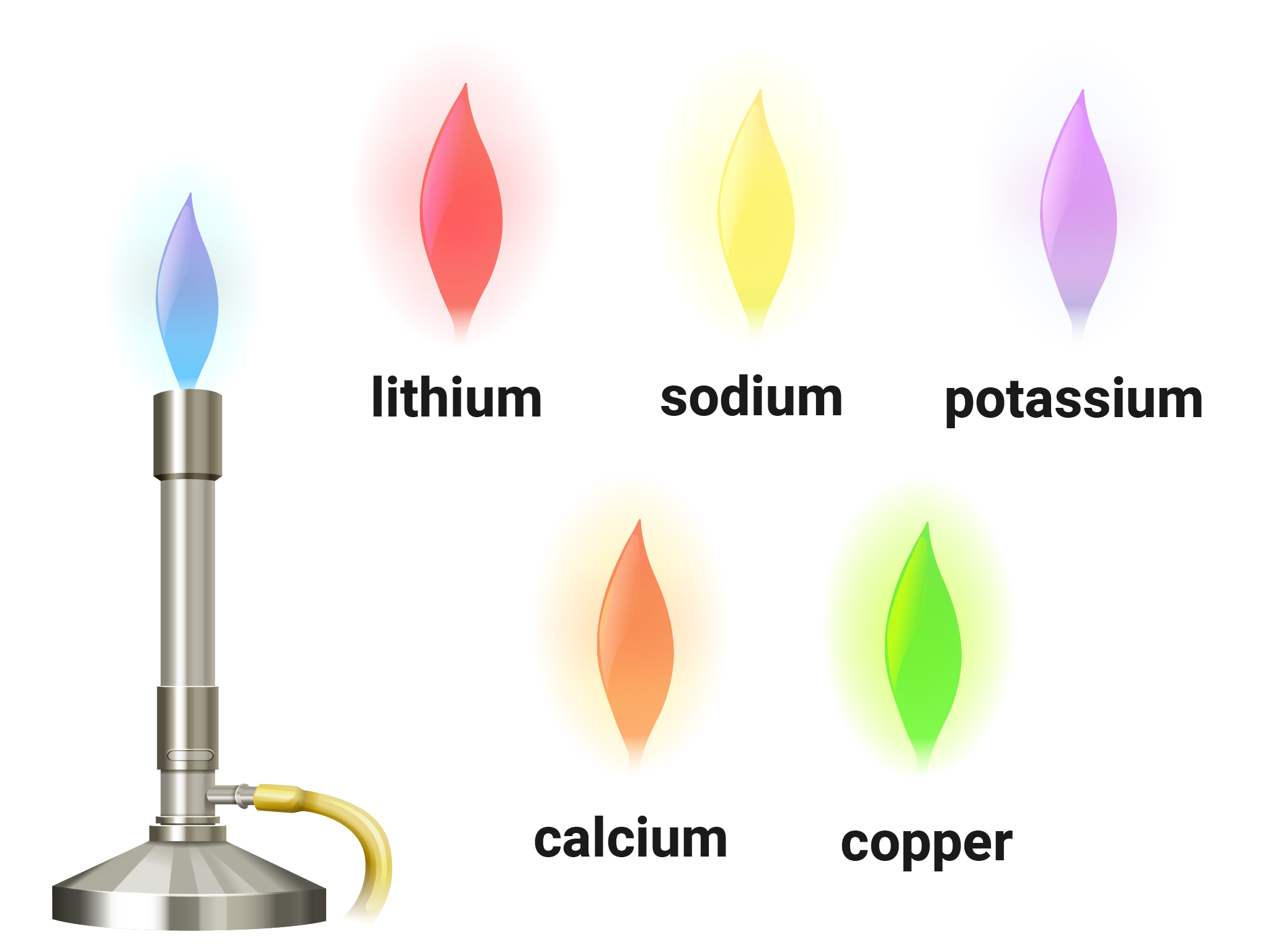
Flame tests can be used to identify metal ions (cations) in compounds. Steps to produce flame colours include:
- wearing eye protection, clean a wire loop by dipping in hydrochloric acid, and then holding in a blue flame for a few seconds
- dip the clean wire loop into a solid sample of the compound being tested, and then hold in a blue flame
- observe and record the flame colour produced
You need to know the colour of :
- lithium ions, Li+ (crimson red)
- sodium ions, Na+ (yellow)
- potassium ion, K+ (lilac)
- calcium ions, Ca2+ (orange-red)
- copper ions, Cu2+ (green)
Testing for Cations
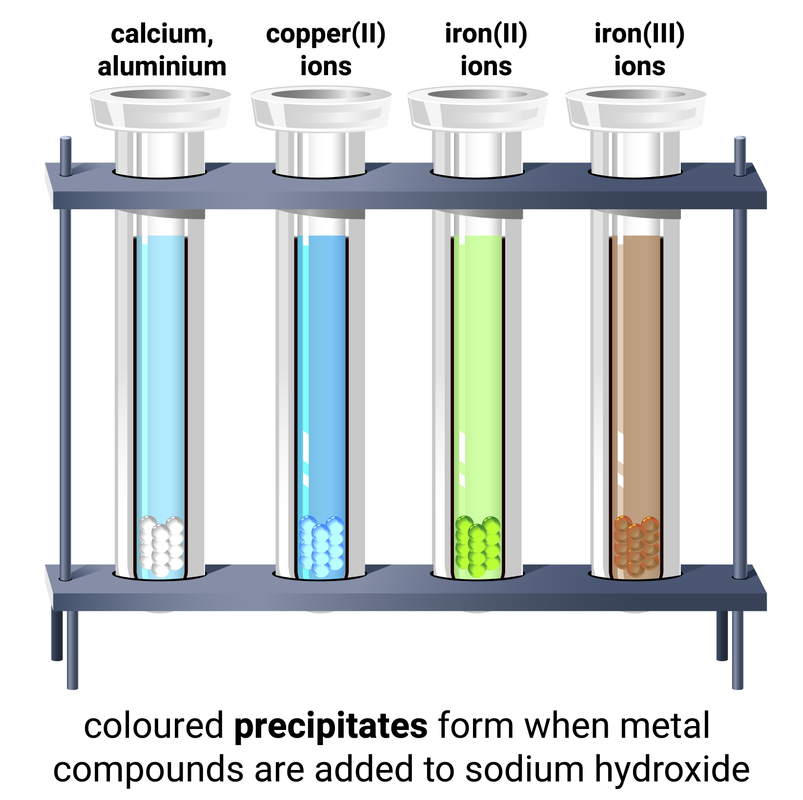
Compounds that contain transition metals are often coloured. If we react two chemicals together and a new solid is made (one that doesn't dissolve in the solution) we call it a precipitation reaction. Compounds can dissociate (split apart into ions) in solutions, and the positive ions are referred to as cations.
Using sodium hydroxide
Dilute sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH) is used to test for some metal ions and can also be used to identify ammonium ions.
| ion | colour of precipitate |
|---|---|
| aluminium, Al3+ |
white adding excess NaOH will cause the precipitate to dissolve |
| calcium, Ca2+ |
white adding excess NaOH does not change the precipitate |
| magnesium, Mg2+ |
white adding excess NaOH does not change the precipitate |
| copper, Cu2+ |
blue |
| iron(II), Fe2+ |
green |
| iron(III), Fe3+ |
brown |
| ammonium, NH4+ |
when warmed will release ammonia gas |
Testing for ammonia
Holding a piece of damp, red litmus paper over ammonia gas will turn the litmus paper blue if ammonia gas is present.
Testing for Anions
Testing for carbonate ions
Carbonate ions, CO32- are detected using any dilute acid (e.g. hydrochloric acid). Bubbles of carbon dioxide gas will be given off when an acid is added.
We can pass the gas through limewater and if it turns the limewater cloudy it will confirm the gas is carbon dioxide.
Testing for sulfate ions
Sulfate ions (SO42-) can be tested for using barium chloride. Barium sulfate will form, which is an insoluble white precipitate.
To test for sulfate ions in solution:
- add a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid to the sample
- add a few drops of dilute barium chloride solution
We add acid first, because carbonate ions will also produce a white precipitate with barium chloride solution. The acid is added so it can react with any carbonate ions that may be present, and so removing them, so they can't give a false result for sulfate ions.
Testing for halide ions
Silver ions will react with halide ions (Cl⁻, Br⁻ or I⁻) to form insoluble precipitates.
To test for halide ions in solution:
- add a few drops of dilute nitric acid to the sample
- add a few drops of dilute silver nitrate solution
- observe and record the colour of any precipitate that forms
We add acid first, because carbonate ions will also produce a white precipitate with silver nitrate solution. The acid is added so it can react with any carbonate ions that may be present, and so removing them, so they can't give a false result for chloride ions.
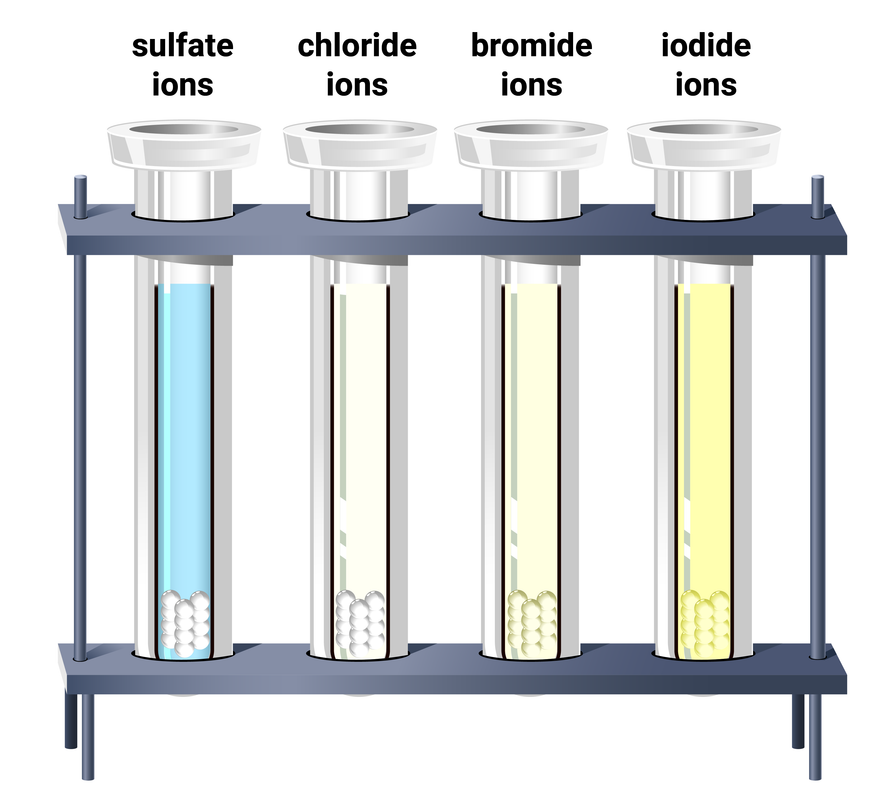
Silver halide precipitates
| ion | colour of precipitate |
|---|---|
| chloride, Cl⁻ |
white |
| bromide, Br⁻ |
cream |
| iodide, I⁻ |
yellow |
Instrumental Methods of Analysis
New technology, developed over the last few decades, have considerably advanced analytical chemistry. These new instrumental methods have three main advantages, they are:
- more rapid (produce results faster)
- more accurate (they are more reliable at identifying elements/compounds)
- more sensitive (they can detect very small amounts of substances)
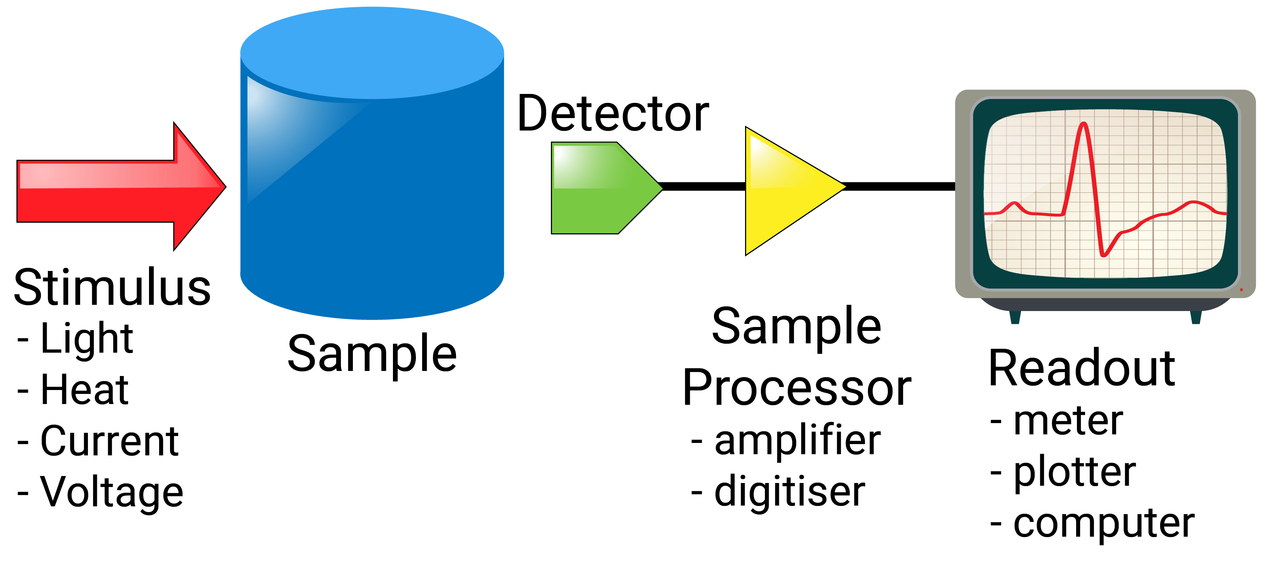
Each method works in a different way, but they essentially have most features in common:
- a stimulus enters the sample (light, heat, current, voltage etc)
- this is then read by a detector, producing a signal
- the signal is amplified/digitalised
- the output is plotted (usually) on a graph
Flame Photometer
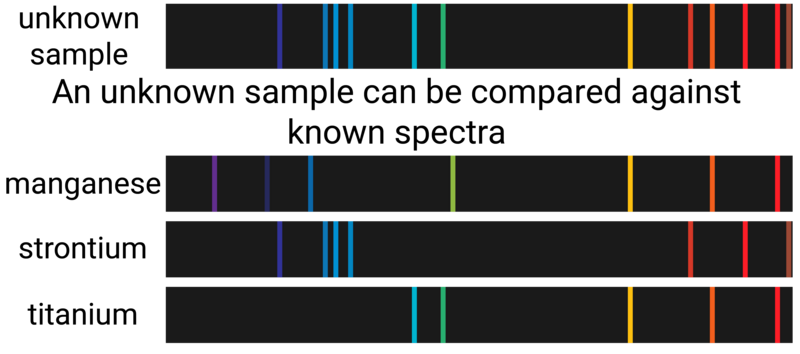
Flame photometers (often referred to as a flame emission spectroscope) is an instrumental method used to analyse metal ions.
- a sample is heated in a flame, and the light emitted from the flame is passed through a spectroscope
- the resulting pattern is known as a spectrum
Every element has its own specific set of wavelengths, so every pattern is unique (can be thought of as an element's 'fingerprint').
If there is a mixture of ions, one colour may be covered up by another in a flame test. In an emission spectrum, the intensity of the light is actually a measure of concentration of the different elements. This means that the ratio of ions present can be determined.
Determining concentrations
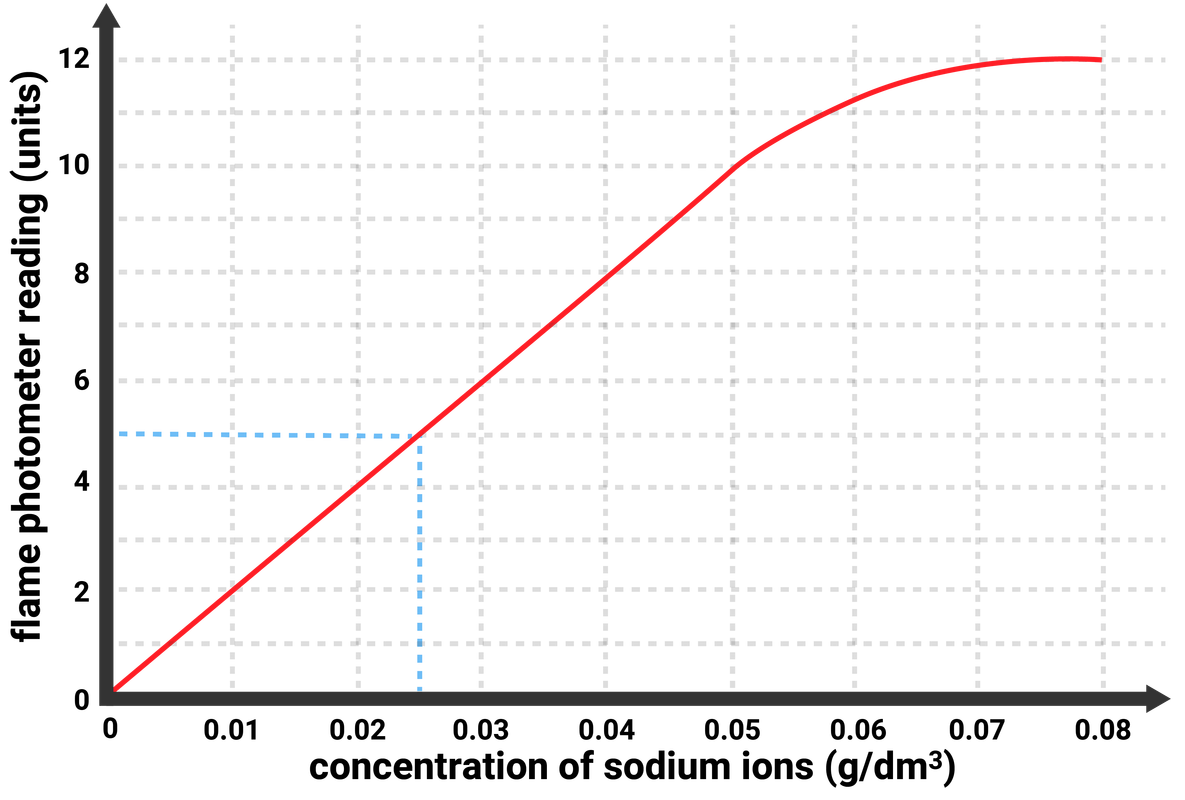
A reading can be taken from the flame photometer for different concentrations of a metal ion in solution. These readings are then used to plot a calibration curve.
Having a calibration curve of known samples, allows scientists to be able to identify the concentration of a sample just by looking at the graph!
For example, if a solution of sodium ions gave a reading of 5 units on the flame photometer, then the calibration curve allows us to read off that the sample had a concentration of 0.025 g/dm3.