
Bulk and Surface Properties of Matter including Nanoparticles
Separate Chemistry 2
Nanoparticles
A nanoparticulate substance is a substance that consists of nanoparticles, and has different properties from the same substance in bulk (powders, lumps and sheets). This is because of the small size and large surface area to volume ratios of the nanoparticles.
An example:
- titanium dioxide blocks ultraviolet light, so it is used in sunscreens
- in bulk, titanium dioxide is white – it is used as a pigment in white paint
- individual particles (nanoparticulate) of titanium dioxide have no colour and cannot be seen when it is spread on skin
The large surface area to volume ratio of nanoparticulates mean they work as great catalysts. Compared to the same substance in bulk, they might:
- be more efficient
- catalyse different reactions
- produce different products
Risks of nanoparticles:
- people are concerned the small size of nanoparticles makes it possible to breathe them in, or to pass into cells
- inside the body, they might catalyse reactions that are harmful producing toxic substances
- modern nanoparticulate materials have not been used for long, so it is difficult for scientists to determine their risks
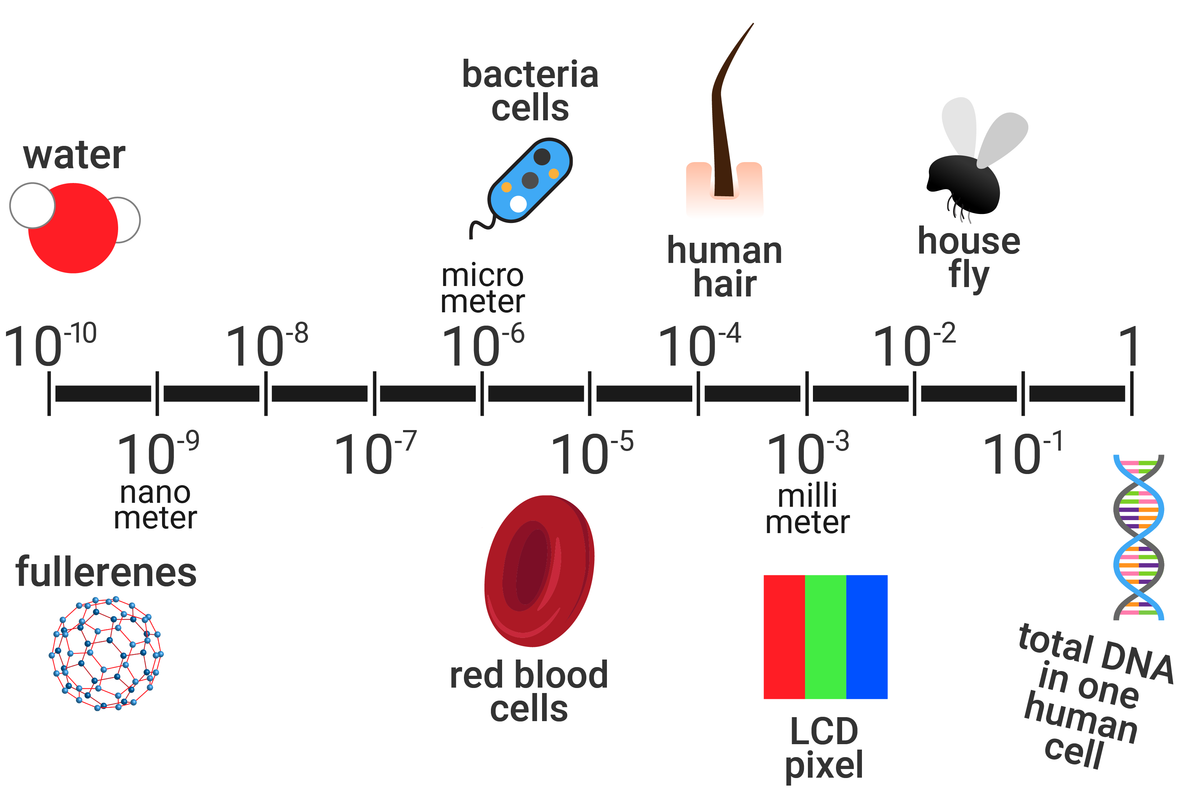
Nanoparticles are about 1-100 nanometres (nm) in size, that contain only a few hundred atoms. Atoms, and simple molecules, are around 100 times smaller than this.
1 nm is 1 x 10-9 m (or 0.000000001 m)
Bulk Materials
Different materials have different properties, and the use of the materials is dependant on these properties.
| glass | clay | metal | polymers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| appearance | transparent | opaque and dull | opaque and shiny | transparent or opaque |
| melting point | high | high | high | high or low |
| malleable or brittle? | brittle | brittle | malleable | malleable or brittle |
| conductor? | poor | poor | good | poor |
Glass ceramics are made by melting sand with other substances (normally metal oxides), then allowing the liquid to cool and solidify.
Clay ceramics are made by heating clay to high temperatures, causing crystals to form and join. Clay ceramics are often normally then coated with a glaze, which hardens on heating. Types of clay ceramic include brick, china and porcelain.
Polymers can be transparent or opaque and they are often tough and flexible, but some are hard and brittle.
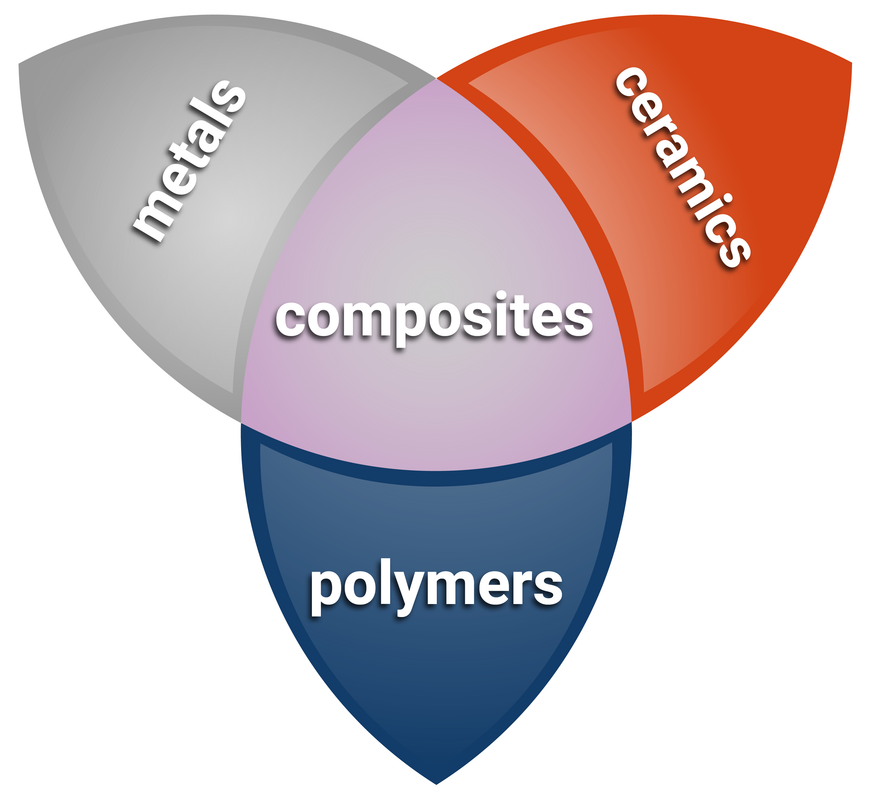
Composites
A composite material consists of two or more materials with different properties to make a new material with more suitable properties. Most composite materials have two components:
- the reinforcement, the substance that makes up the bulk of a composite material
- the matrix, which binds the reinforcement together